User Account Control
| Component of Microsoft Windows | |
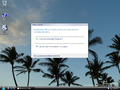
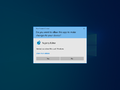
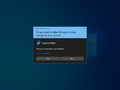
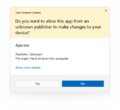
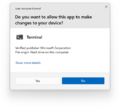
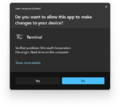
 User Account Control prompting access to Windows Terminal in Windows 11 | |
| Type | Security option |
|---|---|
| Introduced in | Windows Vista |
User Account Control (UAC) is a security feature included in Windows Vista and later, which limits non-compulsory admin applications to standard user privileges unless they are explicitly granted administrator privileges.
Functionality[edit | edit source]
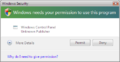
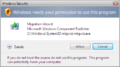
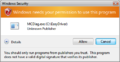
On tasks that requires administrative privileges, the system initializes consent.exe (which shows the UAC prompt) under the SYSTEM account and an application called SSSecure_UAC_Background (which covers the desktop with a dark overlay, also officially referred to as secure desktop). The consent prompt shown by UAC will then provide essential information about the identity of the program alongside with a notice on the top that signifies the security of the program:
- Blue (white in Windows 11) - signed program
- Yellow - unsigned application
- Red - administrator-blocked or certificate-revoked executable (usually happens when the code signing becomes invalid when Windows 10 build 14965.1001 and later expires).
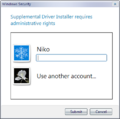
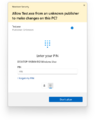
Additionally, it can also display a password prompt if the current user does not hold administrator privileges, requiring an administrator to enter their credentials in order to continue. This is the process of authorizing a program to run at administrator privileges, also called elevation.
The early implementation of UAC (called UAP - User Account Protection) used a different keyword for the administrator privilege request. Unlike the modern implementation, which uses the keyword asInvoker, the early implementations used requireAdministrator instead. This leads to an inability to run modern programs within builds that used this implementation as they will produce a run-time error. It is possible to modify a program's manifest to use the older keyword to trigger the UAP prompt, in turn allowing the program to run correctly. However, programs that perform an integrity verification (such as setups) will not run due to the program's checksum no longer matching the checksum it is verified against.
Elevated processes are then isolated from non-elevated processes by running at a higher integrity level, which prevents most interactions initiated by lower-level processes in order to avoid privilege escalation attacks.
History[edit | edit source]
Windows Longhorn/Vista[edit | edit source]
Pre-reset[edit | edit source]
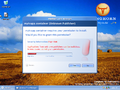
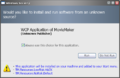
UAC marks its debut as Windows Trust Manager in build 3683 and remains unchanged throughout Milestone 3 and 4. The implementation was rather primitive: only a consent prompt with a bar showing the risk of the program. Additionally, the feature was restricted for Avalon-based applications only.
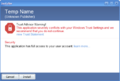
Build 4015 introduces the Windows Trust Advisor, which serves as a successor to the above. When opening an app which the system cannot identify the publisher, the Trust Advisor warns the user that this application severely conflicts with their Windows Trust Settings and that they should not continue.
The feature was nowhere to be seen again in later milestones, only to be brought back again with an another design change in the last pre-reset build.
Post-reset[edit | edit source]
Much like other features that was included with Longhorn, UAC was removed from the development reset builds. It was later reincluded in build 5048, although in a very rudimentary state that features a basic consent prompt that asks the user to run or not to run the program. To enable it, set the following values in the registry:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa]
"LUAEnabled"=dword:00000001
"InstallerDetectionEnabled"=dword:00000001
After that, make a password for the administrator account and create a new limited user account and log into it.
With Windows Vista build 5365.8, Desktop Window Manager effects are now disabled by default and the client area dimmed when a UAC prompt is displayed to the user as a security measure.
Later builds continuously refresh the interface of User Account Control, making it resemble closer and closer to its final form. Additionally, it was called User Account Protection (UAP) and could be enabled or disabled through the use of a Start menu shortcut to toggle.exe. Later, it was renamed to its final name and the settings program is now named UserAccountControlSettings.exe.
Windows 7[edit | edit source]
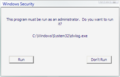
After recieving many user complaints about UAC triggering too often, Microsoft introduced more UAC settings in Windows 7. From that point, UAC could be not only turned off and on, but also could be set not to launch when user changes system settings. The UAC always uses the basic or classic theme unless "Do not dim at my desktop" is on.
Windows 8 to Windows 10[edit | edit source]
The only change from User Account Control since Windows 8 was from Windows 8 build 8066, where the desktop no longer appears when the elevation prompt triggers. Otherwise, the application remained generally unchanged throughout Windows 8 to Windows 10 build 14322.
In Windows 10 build 14328, UAC received major changes based on XAML to comply with the new design language of Windows 10. However, the older UAC dialog design is still present and can be enabled by merging the following value into the registry:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authentication\LogonUI\TestHooks]
"XamlCredUIAvailable"=dword:00000000
The registry key tweak was later removed in subsequent builds.
Additionally, a dark theme for the application was added in Windows 10 build 14342 (rs1_release).
Windows 11[edit | edit source]
User Account Control received a design refresh again to match with the new Fluent design aesthetics introduced with Windows 11.
The 2024 Update largely improves upon the existing User Account Control mechanism by introducing Sudo for Windows, an open-source command-line tool directly inspired by the Unix sudo command, which allows users to run other programs as the root superuser.[1] Despite the name, Sudo for Windows is not based on its Unix counterpart, and is instead written from scratch in the Rust programming language. It does not aim to be compatible with the original implementation either due to the differences between the Windows and Unix permission systems, notably the absence of a superuser account. It can be enabled via the sudo config --enable command, or within a developer-specific toggle included as part of the Settings application.
Sudo for Windows supports multiple modes of operation with varying levels of isolation from unelevated processes. The new window mode merely triggers a User Account Control prompt for the given command and exits. The input disabled and inline modes work by running a second, elevated instance of Sudo itself which runs the given command and redirects its standard streams (excluding the standard input stream if running in input disabled mode) via remote procedure calls to the original, unelevated instance.
With build 27718, the elevation prompt has been changed slightly. In build 27754, the prompt has been slightly updated with the heading and application name in boldface, as well as minor padding and button size adjustments.
Gallery[edit | edit source]
Windows Vista[edit | edit source]
Pre-reset[edit | edit source]
Windows Longhorn build 3683 (Trust Manager prompt)
Windows Longhorn build 4015 (Trust Advisor prompt)
Post-reset and later[edit | edit source]
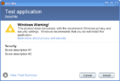
Windows Vista build 5231 (User Account Protection prompt)
Windows 7 to 10[edit | edit source]
Old design[edit | edit source]
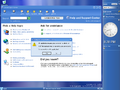
Password prompt in Windows 10 build 11103
New design[edit | edit source]
Windows 10 build 14342 (dark theme)
Windows 10 October 2020 Update (light theme)
Windows 10 October 2020 Update (dark theme)
Windows 11[edit | edit source]
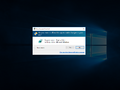
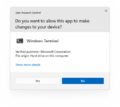
Unsigned app prompt in Windows 11 build 27718
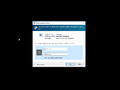
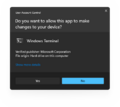
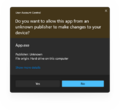
Signed app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754
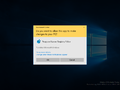
Signed app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754 (dark theme)
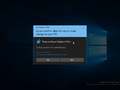
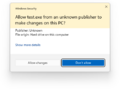
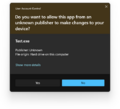
Unsigned app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754
Unsigned app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754 with Administrator protection
Unsigned app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754 (dark theme)
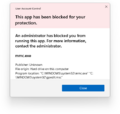
Blocked app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754
Blocked app prompt in Windows 11 build 27754 (dark theme)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Adoumie, Jordi. Introducing Sudo for Windows!, Windows Command Line. 8 February 2024. Retrieved 9 February 2024.