User:Insomnia/Sandbox/3
 Hyper-V running Windows 10, version 22H2 | |
| Type | Hypervisor |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
| Host platform | Windows (x64/ARM64) |
| Guest platform | x86/x64/ARM64 (virtualized) |
| Initial release version | 6.0.6001.18000 (2008-02-27) |
| Latest release version | 10.0.22621.1 (2022-09-20) |
Hyper-V (codenamed Viridian)[1] is a native 64-bit PC-compatible virtualization solution released by Microsoft, and the successor to Virtual PC. It was first included with x64 editions of Windows Server 2008, and has been freely available since Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 as an optional installable component on Pro and higher editions. Its associated graphical user interface, the Hyper-V Manager, is a Microsoft Management Console snap-in.
The hypervisor is also available as part of a separate Windows Server Core operating system release named Hyper-V Server (first introduced alongside Windows Server 2008), which can be used to host virtual machines en masse for applications such as database management, mission critical systems or file storage.
Unlike Virtual PC, Hyper-V is a "level 1 hypervisor" and was therefore unable to coexist with competing solutions like VirtualBox or VMware, which both are "level 2 hypervisors" until the release of the Windows 10 April 2018 Update, which implemented support for the Windows Hypervisor Platform,[2] allowing third-party virtualization software to run and manage virtual machines side-by-side with Hyper-V.[3][4]
Supported guest operating systems[edit | edit source]
This is a definitive list of officially supported operating systems that can run under Hyper-V, as of Windows Server 2025.[5][6]
- Windows 7 with Service Pack 1 and above
- Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 and above
- Most Linux distributions
Deprecated operating systems[edit | edit source]
The following operating systems are supported on older versions of Hyper-V on older host Windows systems, but aren't supported in the latest Windows 11 version of Hyper-V.[7][8]
- Windows 2000 Server with Service Pack 4 (support removed on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012)
- Windows XP with Service Pack 2 or Windows XP Professional x64 Edition with Service Pack 2 (support removed on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016)
- Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (support removed on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016)
- Windows Vista with Service Pack 2 (support removed on Windows 11)
- Windows Small Business Server 2011 (support removed on Windows 11)
- Windows Home Server 2011 (support removed on Windows 11)
- Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 (support removed on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012)
Gallery[edit | edit source]
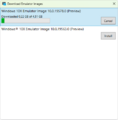
Hyper-V booting Windows 8.1 build 9471
Hyper-V running Windows 10 build 10565
Microsoft Emulator[edit | edit source]
 Manager page | |
| Type | hypervisor |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Host platform | Microsoft Windows |
| Guest platform | x64 |
| Initial release version | 1.1.11.0 |
| Latest release version | 1.1.1081.0 |
| Latest release date | 9 March 2022 |
A stripped-down version of Hyper-V, called Microsoft Emulator has been released to emulate special variants of Windows, such as Windows 10X or the HoloLens 2 firmware.
In contrast to Hyper-V, Microsoft Emulator does not require an ISO file for installing the guest operating system. Instead, it uses "emulator images" in the format of VHDX files. These files can be obtained from the Microsoft Store servers or a designated internal server for internal operating systems. Currently, only the emulator images for two Manganese builds of Windows 10X (build 19563 and build 19578) are available to download publicly.
Gallery[edit | edit source]
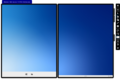
Emulator UI, in this case running Windows 10X build 19578
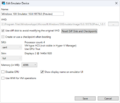
Emulator UI additional tools[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Hyper-V update package end-user license agreement (EULA) in Windows Server 2008 build 6001.16648
- ↑ https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/api/
- ↑ Zongmin. VMware Workstation 15.5 Now Supports Host Hyper-V Mode, VMware Workstation Zealot. 28 May 2020.
- ↑ Oracle. VirtualBox version 6.0 changelog, Oracle VM VirtualBox documentation. 18 December 2020.
- ↑ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/virtualization/hyper-v/supported-windows-guest-operating-systems-for-hyper-v-on-windows
- ↑ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/virtualization/hyper-v/supported-linux-and-freebsd-virtual-machines-for-hyper-v-on-windows
- ↑ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2008-R2-and-2008/cc794868(v=ws.10)
- ↑ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2012-R2-and-2012/dn792028(v=ws.11)