MS-DOS
 | |
 | |
| Developer | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Source model | Closed source for most versions; Open source for versions 1.25, 2.11, and 4.00 |
| Initial release | 86-DOS 0.10 (July 1980) |
| Final release | MS-DOS 8.0 (14 September 2000) |
| Supported platforms | x86 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic |
| User interface | CLI |
| License | Proprietary for most versions; MIT license for versions 1.25, 2.11, and 4.00 |
MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System) is a monolithic singletasking operating system developed by Microsoft between 1980 and 2000 for x86-based personal computers. It was the de facto industry standard environment on the IBM PC and its clones, although it also shipped with other x86-based computers that were incompatible with IBM.
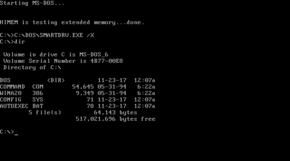
By default, MS-DOS is driven by a command line interface – the A> or C:\> prompt shown when the command processor is ready to accept input ultimately became one of the unofficial symbols of DOS. Several software vendors have developed programs that add a more friendly user interface to manage files and launch other programs. Microsoft itself included such a program, the MS-DOS Shell, with some versions of MS-DOS.
There is very limited support for running multiple programs simultaneously in MS-DOS. The operating system allows a program to terminate and stay resident (TSR), meaning that a portion of the program's code can stay present in memory and be triggered by an API call or a hardware interrupt even after the base program exits. A proper multitasking version of MS-DOS was produced in 1986, however, it only shipped to a limited number of OEMs and eventually evolved into OS/2.
Originally, MS-DOS was not available directly in retail, and was instead distributed by OEMs who licensed it from Microsoft. The manufacturer would receive an OEM Adaptation Kit, which would then be used to build a custom version of MS-DOS with support for a specific machine. However, as the market settled on close to 100% IBM-compatible clones, Microsoft eventually started offering a generic IBM-compatible version of MS-DOS. At first, the generic version was still distributed by the OEMs who bulk-ordered it from Microsoft, although eventually Microsoft started selling MS-DOS directly in retail starting with MS-DOS 5.
The standalone MS-DOS product was eventually discontinued with the release of Windows 95, which integrated MS-DOS into Windows itself in a move that was the subject of a major lawsuit from Caldera, the developer of the competing DR-DOS operating system. The last version, MS-DOS 8, was released in 2000 as a part of Windows Me.
A port of the 16-bit MS-DOS was made for 8-bit MSX computers known as MSX-DOS. MSX-DOS is based on the MS-DOS 1.25 kernel and uses the same filesystem.
Architecture[edit | edit source]
MS-DOS consists of three main components, the DOS BIOS (IO.SYS or IBMBIO.COM), the DOS kernel (MSDOS.SYS or IBMDOS.COM), and the shell (COMMAND.COM). This is the same layout as used by CP/M.
DOS BIOS[edit | edit source]
The DOS BIOS (Basic I/O System) is the lower layer of MS-DOS, which communicates directly with the system's hardware and contains resident device drivers (as opposed to installable drivers, loaded from CONFIG.SYS). This module used to be supplied by an OEM and customized for a particular machine; this practice eventually died out as the market settled on close to 100% IBM-compatible machines.
It also includes the DOS initialization module, SYSINIT, which is invoked by the boot sector when booting into MS-DOS. The module initializes the DOS BIOS as well as the DOS kernel, parses the CONFIG.SYS file and then proceeds to launch the shell.
DOS kernel[edit | edit source]
The DOS kernel is the higher layer of MS-DOS, and provides services including process control, memory management, and file system access. It is equivalent to the Basic Disk Operating System component of CP/M.
Process control functionality is very limited due to the system's single-tasking nature. A program can execute another program, although control will not return to the original program until the other program exits. A program can, however, choose to terminate and stay resident (TSR), which leaves a portion of the program present in memory. If the program hooks an interrupt handler before terminating this way, the resident part can get called even when other programs are running, creating an illusion of multitasking.
Memory management allows programs to allocate conventional memory at runtime as needed. It is necessary when multiple programs are loaded to make sure that the active program does not overwrite the data of the other programs. However, as MS-DOS runs in real mode, there is no memory protection and therefore the allocations are not actually enforced, unlike protected mode operating systems.
The kernel implements support for File Allocation Table (FAT) family file systems. The original FAT12 file system was adapted from the file system used by Microsoft Standalone Disk BASIC and used 12-bit cluster indices. In the following versions, it was further improved by adding support for subdirectories and larger volumes, and by extending the FAT to use 16-bit and later 32-bit cluster indices. The file system implementation in the MS-DOS kernel is completely bypassed when running DOS applications under Windows for Workgroups 3.11 or later with 32-bit file access enabled; the VFAT virtual driver that implements the feature was later improved in Windows 95 to support long file names.
The redirector interface, introduced with MS-DOS 3.1, allows bypassing the FAT file system code to implement a custom file system. This was originally intended to be used by network clients as a means of enabling access to files on other networked computers, although it was eventually also used to implement support for the CD-ROM file system in the Microsoft CD-ROM Extensions (MSCDEX).
Since MS-DOS 7, the kernel has been merged into IO.SYS, while MSDOS.SYS serves as a configuration file.
Source code[edit | edit source]
An incomplete copy of the source code for a beta version of MS-DOS 6 leaked online in 2000. A copy of the MS-DOS 3.30 OEM Adaptation Kit, the source kit used by computer vendors to customize MS-DOS for their hardware, has also been uploaded online in the past.
In 2014, the source code of MS-DOS 1.25 (equivalent to PC DOS 1.1) and 2.11 was released via the Computer History Museum for non-commercial purposes.[1] Microsoft later re-released the source code on GitHub under the permissive MIT license in 2018. The source code for MS-DOS 1.25 was contributed by Tim Paterson and comes from the Seattle Computer Products OEM version. It includes the source code for SCP's IO.SYS and other SCP tools.[2] The files included in the MS-DOS 2.11 source code release come from at least three distinct sources: MS-DOS 2.00 OEM distribution disks, MS-DOS 2.11 source code of unknown provenance and miscellaneous debris such as WordStar 3.20 overlay files.[3]
The source code for MS-DOS 4.00 was released in 2024 also under the MIT license,[4] together with a beta version of Multitasking MS-DOS 4 including internal design documents and driver source code.[5]
Timeline[edit | edit source]
| Name | Initial release | Last update | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 86-DOS | 0.10 (1980) | 1.14 (1981) | Internally known as QDOS (Quick and Dirty Operating System) |
| MS-DOS 1 | 1.20 (1981) | 1.54 (1982) | — |
| MS-DOS 2 | 2.00 (1983) | 2.25 (1985) | — |
| MS-DOS 3 | 3.00 (1984) | 3.31 (1987) | — |
| Multitasking MS-DOS 4 | 4.00 (1985) | 4.10 (1987) | Also known as European MS-DOS 4; later evolved into OS/2 |
| MS-DOS 4 | 4.00 (1988) | 4.01 (1988) | — |
| MS-DOS 5 | 5.00 (1991) | 5.00A-H (1991) | First version developed without participation from IBM |
| MS-DOS 6 | 6.00 (1993) | 6.22 (1994) | — |
| MS-DOS 7 | 7.00 (1995) | 7.10 (1996) | Included with Windows 95; 7.10 was later included with 95 OSR2 as well as Windows 98 |
| MS-DOS 8 | 8.00 (2000) | 8.00 (2000) | Included with Windows Me and used for the startup disk option in Windows XP through Windows 8.1 |
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ https://computerhistory.org/blog/microsoft-ms-dos-early-source-code/
- ↑ https://www.os2museum.com/wp/pc-dos-1-1-from-scratch/
- ↑ https://www.os2museum.com/wp/dos-2-11-from-scratch/
- ↑ https://github.com/microsoft/MS-DOS/pull/431
- ↑ https://github.com/microsoft/MS-DOS/commit/69417b9befa431b12f495e03d97ae836039a4bbf