Windows Subsystem for Android
| Component of Microsoft Windows | |
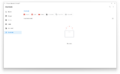
 Launch screen | |
| Introduced in | Windows 11 |
|---|---|
Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) was a compatibility layer on top of Windows 11, which enables the ability to run Android applications.
Background[edit | edit source]
Windows Subsystem for Android was first confirmed at the "What's Next for Windows" event on 24 June 2021, right after the announcement for Windows 11.[1] It was later publicly introduced in the United States on 20 October 2021,[2] with the first preview version available to Windows Insiders in the Beta Channel on the same day.[3] It was later released to Insiders in the Dev Channel on 11 November 2021, and to Insiders in the Release Preview Channel on 26 January 2022, respectively.[3] It was released to Windows Insiders in Japan on 18 August 2022.[4] It also utilizes Intel Bridge Technology, a runtime post-compiler for running ARM apps on x86 based processors.
Windows Subsystem for Android was deprecated on 5 March 2024,[5] and will cease to function on 5 March 2025. While Microsoft did not provide an official reason for the deprecation, Andrew Clinick, a former developer who worked on WSA, stated that the lack of revenue from Microsoft Store and absence of Google Play Services support limiting number of usable applications were the reasons behind the deprecation.[6]
System requirements[edit | edit source]
| Memory | 8 GB (minimum) 16 GB (recommended) |
|---|---|
| Storage type | Solid State Drive (SSD) |
| Processor (minimum) |
Intel Coffee Lake (8th Gen) Core i3 series AMD Ryzen 3000 Qualcomm Snapdragon 8c |
| Screen (minimum) |
720p (1280×720) with a 9 inch screen or above |
Guide[edit | edit source]
There are two methods to install Android apps:
- Obtain apps available in the Amazon Appstore, which can be installed from Microsoft Store.
- Sideload apps by using Android Debug Bridge (ADB) to install any standard Android app installation package (
.apk).
Gallery[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Join us to see what’s next for developers
- ↑ Introducing Android™ Apps on Windows 11 to Windows Insiders
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Announcing Android™ apps on Windows 11 Preview for Windows Insiders in the Beta Channel
- ↑ Expanding Android™ Apps on Windows 11 to Windows Insiders in Japan
- ↑ Wojo, Matt et al. Windows Subsystem for Android main page, Microsoft Learn. 5 March 2024.
- ↑ Parmar, Mayank (2024-03-07). "Windows 11's Android project allegedly shelved due to insufficient Store revenue". Windows Latest. Retrieved 2024-04-29.