Windows 95 20 July 1992 build
| Build of Windows 95 | |
 | |
| OS family | 16-bit Windows |
|---|---|
| Version number | 3.10 |
| Build number | 07200022 |
| Architecture | x86 PC/AT (16 bit) |
| Compiled on | 1992-07-20 |
| About dialog | |
The 20 July 1992 build or build 07200022 is the earliest confirmed and available build of Windows 95, which predates the Chicago Feature Specification document by more than 2 months.[1] It was originally leaked on 18 September 1992 as a mislabeled Windows for Workgroups 3.1 build, and was later rediscovered and reuploaded on 23 June 2024.[2]
This build is relatively similar to contemporary builds of Windows for Workgroups 3.1, although it includes a number of user experience changes such as the new 3D control style, new applications and updated versions of existing applications. Unlike later builds of Windows 95, it requires a version of MS-DOS to be already installed and does not include any Win32 support, notably predating the earliest publicly released Win32s beta.
Build number[edit | edit source]
This build uses an unusual build number format where the first four digits are the date when the build was compiled. Therefore, build number 07200022 means that the build was compiled on 20 July. The latter four digits could be the time that this build was compiled, which would correspond to 00:22. This would match the file modified times seen in the available copy, although it was common for Microsoft to tamper with file modified times and should not be considered authoritative. It is possible that the second part could still be the traditional, consecutive build number.
This format appears to have continued to be used after the version number was increased to 4.0; Windows for Workgroups 3.11 build 026 includes several components backported from Chicago and/or Cougar builds, including SVGA256.DRV with a version number of 4.00.08310026 (later builds of Windows for Workgroups 3.11 include updated versions of this component sourced from later Chicago builds).
Relationship to various projects[edit | edit source]
It is disputed whether this build was indeed compiled as a part of the Chicago project, or a smaller project that ended up being overtaken by Chicago. The build was compiled more than two months before the Chicago Feature Specification was finished,[1] although the project was already well underway as shown by an internal e-mail discussing user interface change planning that went out in June 1992,[3] more than a month prior to the compilation of this build. Certain features mentioned in the feature specification, such as a generic 256 color SVGA driver, are already implemented in this build.
The build was compiled and packaged in a similar fashion to a regular Windows for Workgroups 3.1 build, which led to it being mislabeled as one when it originally leaked. Likely as a result of this, the build functions well on top of standard, standalone MS-DOS for the most part. However, the WinOldAp module that enables running MS-DOS applications under Windows depends on functionality that was implemented by Cougar, the 32-bit DOS kernel project, and is therefore broken under this copy of the build. It is possible that Win32 support is absent because it depends on features added in Cougar which are also absent.
A Win32 DLL from an early version of Win32s from January 1992 is included with the build. However, it sits unused as the build includes no Win32 implementation at all. The library is actually referenced in dead code within KERNEL32.DLL from build 58s, although it does not exist in that build. This still suggests that Win32c, the subset of Win32 implemented in Chicago was indeed derived from Win32s.
New features and changes[edit | edit source]
User interface[edit | edit source]
The user interface in this build has been redesigned to make its three-dimensional items more visible to the naked eye. Various other user interface elements have reverted their bold font style and have gone to their regular font states as well.
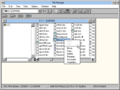
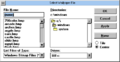
File Manager[edit | edit source]
There are two versions of the File Manager in this build – an unmodified Windows 3.1 WINFILE.EXE and a new FILEMAN.EXE. The main new feature added to this variant of File Manager is that it has right-click menus for files, folders and drives (something that would later become part of the Windows 95 user interface guidelines), allowing the user to do various context-specific file actions, such as moving, copying, deleting, renaming, and viewing file properties, as well as associating a file extension with an application.
The new version of File Manager also writes a different boot sector to a floppy disk when formatting it. It also has additional strings "Moving...", "Copying..." and "Deleting..." that don't appear to be used anywhere in the code yet.
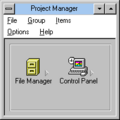
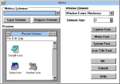
Item / Project Manager[edit | edit source]
While calling itself "Windows Item Manager" in its executable header, it appears to be a very cut down Program Manager alternative. The user can add items to group windows and open .GRP files created by Program Manager. However, .GRP files produced by Project Manager cannot be loaded by Program Manager.
Raster[edit | edit source]
A redesigned version of the Paintbrush application, being built upon the Microsoft Foundation Class Library, is included in this build. Raster overhauls the user experience compared to Paintbrush, having smaller tool buttons, and a wider arrange of colours in the colour palette. Controlling all of the settings in Raster is done via the menu bar, unlike later builds where some are instead bundled with the tool buttons itself. It is a 16-bit application and still uses the Windows 3-style common controls, though the UI is an early version of that seen in Paint in builds 89 and later of Windows 95.
Task List[edit | edit source]
An early version of the Windows 95 Task List is included, replacing the Windows 3.x version. This version adds application icons for each app and a menu bar, however some options, such as ending tasks and the run box are not functional.
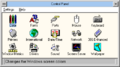
Control Panel[edit | edit source]
- The "Metrics" control panel option is present (
METRICS.CPL), although not installed by default. It is similar to the one from build 58s. - The "Desktop" control panel option has been removed, being replaced by a wallpaper selector (
WALL.CPL) and a screensaver control panel option similar to one from Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions 1.0 (SSDLG.CPL), both not installed by default.
Drag and Drop Printing[edit | edit source]
Drag and Drop Printing is a program that creates an icon for the printers installed on your system and allows you to print just by dragging a file on top of them. Double clicking on the icon opens a configuration UI for the printer. If you drag a file that can't be printed, it refers to itself as "Print Dropper".
WinOldAp[edit | edit source]
This copy of the build ships with a version of WINOA386.MOD that depends on functionality that was implemented as a part of Cougar, the 32-bit DOS kernel project. Running MS-DOS applications under 386 Enhanced Mode is therefore broken and launching one will cause errors.
The executable includes resources for a toolbar in windowed mode, which was later observed in build 58s. TrueType font support in windowed mode and "stream-oriented cut and paste", both mentioned in the Chicago Feature Specification as Cougar improvements, were also being worked on at this time. The executable description for WINOA386.MOD replaced "WIN386" with "DOS386", a change that also carried over to later builds of Windows 95.
Cougar dependency[edit | edit source]
Compared to Windows for Workgroups 3.1 build 014e, WINOA386.MOD in this build features extra code in its initialization function (cseg02:8099) that is not present in build 014e (cseg02:0049).
Notably, the version included with this build makes calls to the WSHELL virtual device driver, which was split away from the SHELL VxD during the development of Cougar in anticipation of a standalone, 32-bit MS-DOS version.[4] It also makes use of a new function to get a VxD API by its name rather than ID and checks for version number 3.20 rather than 3.10. In addition, the included VGA DOS-mode video driver for WINOA386, VGA.3GR, checks for VDDVGA version number 3.11 rather than 3.10.
Windows for Workgroups 3.1 build 014e WINOA386.MOD disassembly
; 014e cseg02:0166 mov ax, 1683h cseg02:0169 int 2Fh ; - Multiplex - MS WINDOWS - 3+ - GET CURRENT VIRTUAL MACHINE ID cseg02:0169 ; Return: BX = current virtual machine (VM) ID cseg02:016B cmp bl, 1 cseg02:016E jz short running_in_first_vm cseg02:0170 cseg02:0170 error: cseg02:0170 mov ax, 6 cseg02:0173 cseg02:0173 error_2: ; ... cseg02:0187 running_in_first_vm: ; CODE XREF: sub_6A89+125↑j cseg02:0187 mov bx, 17h ; vxd id: SHELL cseg02:018A mov ax, 1684h cseg02:018D int 2Fh ; - Multiplex - MS WINDOWS - GET DEVICE API ENTRY POINT cseg02:018D ; BX = virtual device (VxD) ID, ES:DI = 0000h:0000h cseg02:018D ; Return: ES:DI -> VxD API entry point, or 0:0 if the VxD does not support an API cseg02:018F mov word ptr g_shell_api, di cseg02:0193 mov word ptr g_shell_api+2, es cseg02:0197 cmp g_shell_api, 0 cseg02:019D jz short error cseg02:019F mov edx, 0 cseg02:01A5 call g_shell_api cseg02:01A9 jb short error cseg02:01AB cmp eax, 30Ah ; version number 3.10 cseg02:01B1 mov ax, 0Bh cseg02:01B4 jnz short error_2
Build 07200022 WINOA386.MOD disassembly
cseg02:09A6 mov ax, 1683h cseg02:09A9 int 2Fh ; - Multiplex - MS WINDOWS - 3+ - GET CURRENT VIRTUAL MACHINE ID cseg02:09A9 ; Return: BX = current virtual machine (VM) ID cseg02:09AB cmp bl, 1 cseg02:09AE jz short running_in_first_vm cseg02:09B0 cseg02:09B0 error: ; CODE XREF: sub_8099+103↑j cseg02:09B0 ; sub_8099+15B↓j ... cseg02:09B0 mov ax, 6 cseg02:09B3 cseg02:09B3 error_2: ; ... cseg02:09C7 running_in_first_vm: ; CODE XREF: sub_8099+125↑j cseg02:09C7 xor bx, bx cseg02:09C9 mov ax, seg dseg03 cseg02:09CC mov es, ax cseg02:09CE assume es:dseg03 cseg02:09CE mov di, offset aWshell ; "WSHELL " cseg02:09D1 mov ax, 1684h cseg02:09D4 int 2Fh ; - Multiplex - MS WINDOWS - GET DEVICE API ENTRY POINT cseg02:09D4 ; BX = virtual device (VxD) ID, ES:DI = 0000h:0000h cseg02:09D4 ; Return: ES:DI -> VxD API entry point, or 0:0 if the VxD does not support an API cseg02:09D6 mov word ptr g_wshell_api, di cseg02:09DA mov word ptr g_wshell_api+2, es cseg02:09DE cmp g_wshell_api, 0 cseg02:09E4 jz short error cseg02:09E6 mov bx, 17h ; vxd id: SHELL cseg02:09E9 mov ax, 1684h cseg02:09EC int 2Fh ; - Multiplex - MS WINDOWS - GET DEVICE API ENTRY POINT cseg02:09EC ; BX = virtual device (VxD) ID, ES:DI = 0000h:0000h cseg02:09EC ; Return: ES:DI -> VxD API entry point, or 0:0 if the VxD does not support an API cseg02:09EE mov word ptr g_shell_api, di cseg02:09F2 mov word ptr g_shell_api+2, es cseg02:09F6 cmp g_shell_api, 0 cseg02:09FC jz short error cseg02:09FE mov edx, 0 cseg02:0A04 call g_wshell_api cseg02:0A08 jb short error cseg02:0A0A cmp eax, 314h ; version number 3.20 (!!!!) cseg02:0A10 mov ax, 0Bh cseg02:0A13 jnz short error_2
Windows Memory Viewer[edit | edit source]
An application called Windows Memory Viewer (WINMEM.EXE) is present on the install media, however the driver it requires to run, MEMINFO.386, is not. By patching the application to not look for the driver in question, it is possible for it to run successfully.
256 color generic SVGA driver[edit | edit source]
This build includes SVGA256.DRV, a generic 256 color super VGA driver mentioned in the Feature Specification.
MS32EM87[edit | edit source]
This build includes an entirely unused MS32EM87.DLL, which is a PE using the old NT build 196 header format (although the first section header is zeroed out). As the name suggests, it is an Intel 80387 floating point emulator; exporting symbols _Ms32KrnlCbDataSize and _Ms32KrnlHandler, and importing two functions by ordinal from MS32Krnl. CodeView symbols are included; the executable was linked from two modules: \mrt32\emulator\objs\emdos32.obj and \mrt32\emulator\386\emulator.asm.
Unreferenced dead code in KERNEL32.DLL from build 58s will attempt to load MS32EM87.DLL, which does not exist in that build.
This component appears to be from a very early build of Win32s (PE build timestamp is Thu Jan 09 1992 05:32:23 GMT+0000); the build of Win32s included with the SDK of Windows NT 3.1 build 340 renamed it to W32SEM87.DLL and the DLL being imported from to W32SKRNL.DLL; and later builds of Win32s removed the file entirely.
New system APIs[edit | edit source]
KERNEL[edit | edit source]
System functionality has been implemented to read and write structs to INI files, using the READPRIVATEPROFILESTRUCT and WRITEPRIVATEPROFILESTRUCT KRNL386.EXE functions (these functions do not exist in the standard mode KRNL286.EXE, which is in fact unmodified from Windows for Workgroups 3.1 build 014e, perhaps indicating dropping Standard Mode Windows was already planned as of this build).
GDI[edit | edit source]
GDI.EXE has new exports mentioned in the Feature Specification: PolyBezier, PolyBezierTo and CreateDibSection.
USER[edit | edit source]
USER.EXE has a new DrawFrameControl export mentioned in the Feature Specification.
SHELL[edit | edit source]
SHELL.DLL has a new LOCATEHOOKPROC export.
Bugs and quirks[edit | edit source]
As this build is quite early in development, there are a few bugs and quirks in this build.
Networking[edit | edit source]
Networking functionality is quite buggy in this build, and as a result the system may crash on startup. It is recommended to either remove the network part of the [386Enh] section in SYSTEM.INI, or boot in standard mode to avoid loading buggy virtual device drivers.
Screensavers[edit | edit source]
- Attempting to configure or test the "Blank Screen" screensaver will cause an error in the applet, however if clicking Ignore afterwards, it does the intended action.
- Closing the applet crashes Control Panel.
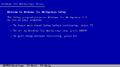
MS-DOS application support[edit | edit source]
Trying to open an MS-DOS Prompt or any other DOS application in 386 enhanced mode will fail with a "Windows not set up correctly. Run the Windows Setup program again or run Windows in standard mode." error message. This is caused by the WinOldAp module for this mode (WINOA386.MOD) expecting to run under Cougar and calling into virtual device drivers not present in this build.
Graphics[edit | edit source]
- In colour modes higher than 256 colours, Windows will report to be low on memory, and as a result will display most icons in the Program Manager as black boxes.
- In 16 colour mode, the title bar font during Windows Setup will be Fixedsys instead of MS Sans Serif.
Applications[edit | edit source]
- The Paging Heap Viewer will throw out a General Protection Fault when trying to run it on this build.
- Paging statistics in the Windows Memory Viewer will not work, presumably due to
MEMINFO.386being missing.